Jungwon Yoon (2020)
Design-to-fabrication with thermo-responsive shape memory polymer applications for building skins,
Architectural Science Review, DOI: 10.1080/00038628.2020.1742644
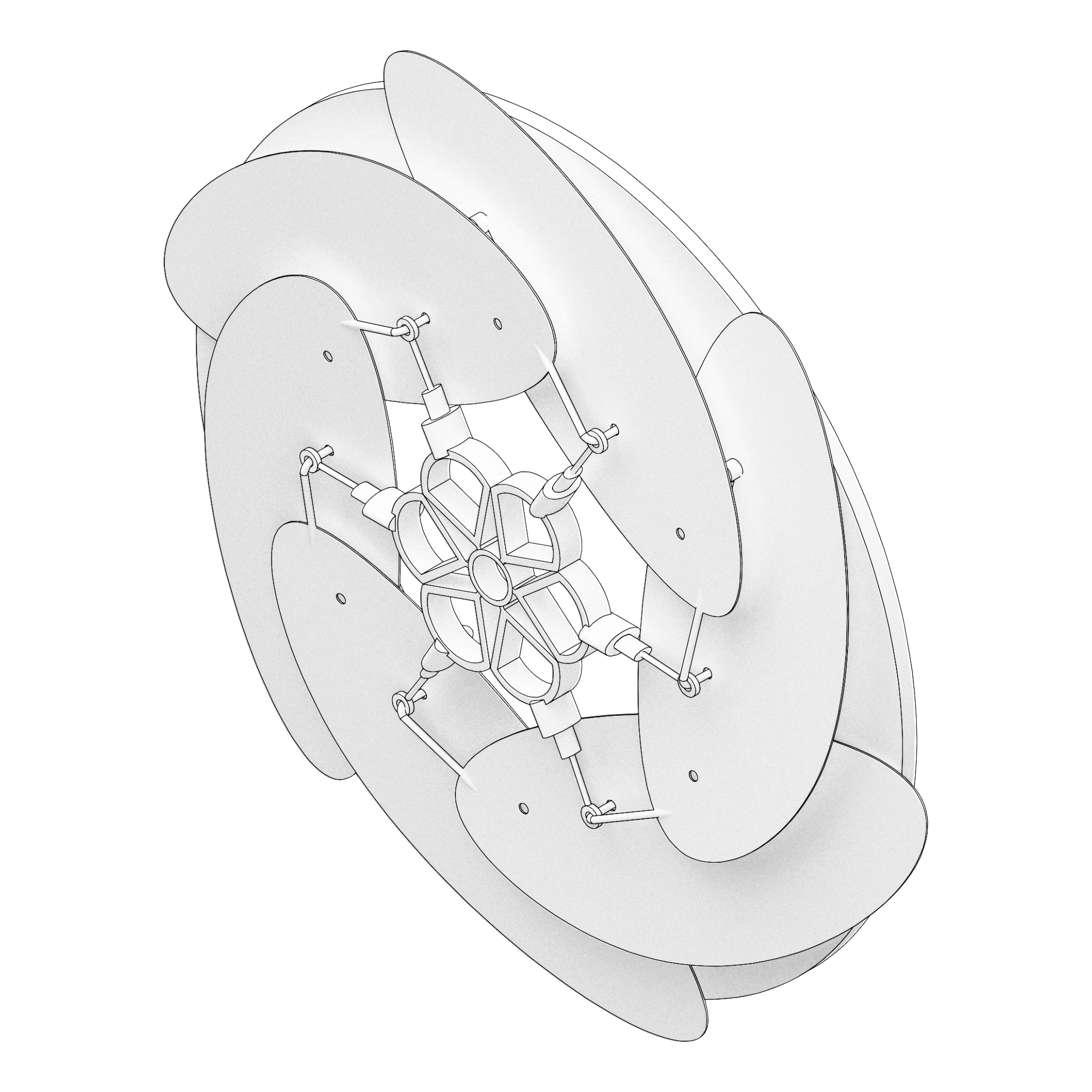
Acknowledgement: The figure above is derived in part from the manuscript in Architectural Science Review <copyright Taylor & Francis>
The Version of Record of this manuscript has been published and is available in Architectural Science Review, https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00038628.2020.1742644?scroll=top&needAccess=true
Design-to-fabrication with thermo-responsive shape memory polymer applications for building skins
(2020). Design-to-fabrication with thermo-responsive shape memory polymer applications for building skins. Architectural Science Review. Ahead of Print.
www.tandfonline.com
ABSTRACT
Smart materials are studied for climate-responsive building skins due to internal changeable properties stimulated by material-specific input. This research focuses on shape memory polymer (SMP) and temperature as its activating stimulus for dynamic shading devices with mechanisms of opening and closing. From case-studies, four design strategies are presented in this paper. Design research and 3D printing fabrication tests of SMP prototypes were conducted by the research-through-design approach. Prototypes were comparatively analyzed for development and optimization in architectural applications. It is challenging to train permanent shapes, to program temporary shapes and to design repetitive material behaviours. Measures to achieve reversible reiterative shape-changing materials are required for practical implementation. For further design-fabrication research on the actual temperature and the material behaviours of designed elements, the SMP with glass transition at 35°C was applied. Later, it would be necessary to simulate the environmental effects and validate the performance of thermo-responsive SMP building skins.
KEYWORDS
Climate-adaptive, thermo-responsive, shape memory polymer (SMP), building skin, shading, fabrication
This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning: [grant number NRF-2017R1C1B5015080].

Download Link: https://www.tandfonline.com/eprint/CVXJUE5HQZXUSNJVNMII/full?target=10.1080/00038628.2020.1742644
'Publication > Journals and Papers' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Performance Evaluation and Design of Thermo-Responsive SMP Shading Prototypes (1) | 2020.05.28 |
|---|---|
| SMP Prototype Design and Fabrication for Thermo-responsive Façade Elements (2) | 2019.04.09 |


